Dvojný integrál
1 Kvadratický moment pro obdélník
Vypočtěte integrál \[ \begin{aligned} \iint_\Omega y^2\,\mathrm dx \mathrm dy,\\ \end{aligned} \] přes obdélník se stranami podél os, se středem v počátku a délkou stran \(\displaystyle a\) a \(\displaystyle b\), tj. přes množinu \(\displaystyle \Omega\) danou nerovnostmi \[ \begin{aligned} -\frac a2\leq &x\leq \frac a2,\\ -\frac b2\leq &y \leq \frac b2. \end{aligned} \]
Řešení
\[ \begin{aligned} \iint_\Omega y^2\,\mathrm dx \mathrm dy = \int_{-\frac a2}^{\frac a2} \,\mathrm dx \times \int_{-\frac b2}^{\frac b2}y^2\,\mathrm dy=a\times \left[\frac 13 y^3\right]_{-\frac b2}^{\frac b2}=a\times \left(\frac 13 \times \frac {b^3}{8} + \frac 13 \times \frac {b^3}{8}\right)= \frac 1{12}ab^3 \end{aligned} \]
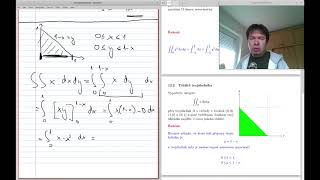
2 Těžiště trojúhelníku
Vypočtěte integrál \[ \iint_\Omega x\,\mathrm dx \mathrm dy \] přes trojúhelník \(\displaystyle \Omega\) s vrcholy v bodech \(\displaystyle (0,0)\), \(\displaystyle (1,0)\) a \(\displaystyle (0,1)\) a poté vydělením obsahem trojúhleníka najděte \(\displaystyle x\)-ovou polohu těžiště.
Řešení
Rovnice přímky, ve které leží přepona trojúhelníka, je \[y=1-x\] a trojúhelník tedy je možno zapsat soustavou nerovností
\[ \begin{aligned} 0\leq &x\leq 1,\\ 0\leq &y \leq 1-x. \end{aligned} \]
Použitím těchto nerovností můžeme dvojný integrál transformovat na dvojnásobný a vypočítat. \[ \begin{aligned} \iint_\Omega x\,\mathrm dx\mathrm dy &=\int_0^1 \int_0^{1-x} x\,\mathrm dy\mathrm dx =\int_0^1 \left[xy\right]_0^{1-x}\,\mathrm dx =\int_0^1 x(1-x)\,\mathrm dx \\&=\int_0^1 x-x^2\,\mathrm dx =\left[\frac 12 x^2 - \frac 13 x^3\right]_0^1 \\&=\frac 12 -\frac 13 =\frac 1{6} \end{aligned} \]
\[x_T=\frac{\frac 16}{\frac 12}=\frac 13\]
3 Velikost tlakové síly na hráz přehrady
Viz video ke cvičení a text k přednášce.
4 Působiště tlakové síly na hráz přehrady
Viz video ke cvičení a text k přednášce.
 Youtube cvičení
Youtube cvičení