Sage Quick Reference
GNU Free Document License, extend for your own use
Aim: map standard math notation to Sage commands
Based on PDF refcards from Sage Wiki
(see the link above for names of authors of these refcards)
(see README for information about sources and customization of this
document)
Contents
1.1 Notebook
1.2 Command line
1.3 Numbers
1.4 Arithmetic
1.5 Builtin constants and functions
2 Symbolic expressions and operations on expressions
2.1 Symbolic expressions
2.2 Defining symbolic expressions
2.3 Symbolic functions
2.4 Python functions
2.5 Simplifying and expanding
2.6 Equations
2.7 Factorization
3 Calculus
3.1 Limits
3.2 Derivatives
3.3 Integrals
3.4 Taylor and partial fraction expansion
3.5 Numerical roots and optimization
3.6 Multivariable calculus
4 Graphics
4.1 2D graphics
4.2 3D graphics
5 Matrices
5.1 Basic matrix algebra
5.2 Matrix Constructions
5.3 Matrix Multiplication
5.4 Matrix Spaces
5.5 Matrix Operations
5.6 Row Operations
5.7 Echelon Form
5.8 Pieces of Matrices
5.9 Combining Matrices
5.10 Scalar Functions on Matrices
5.11 MatrixProperties
5.12 Eigenvalues
5.13 Solutions to Systems
6 Linear algebra
6.1 Vector Constructions
6.2 Vector Operations
6.3 Vector Spaces
6.4 Vector Space Properties
6.5 Constructing Subspaces
6.6 Dense versus Sparse
6.7 Rings
6.8 Vector Spaces versus Modules
7 Specials
7.1 Python modules
7.2 Profiling and debugging
1 Main system
1.1 Notebook
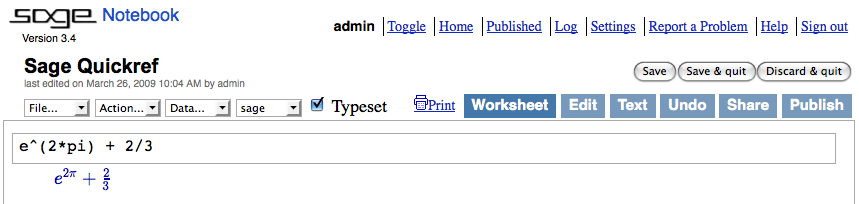
Evaluate cell: \( \displaystyle \langle \) shift-enter\( \displaystyle \rangle \)
Evaluate cell creating new cell: \( \displaystyle \langle \) alt-enter\( \displaystyle \rangle \)
Split cell: \( \displaystyle \langle \) control-;\( \displaystyle \rangle \)
Join cells: \( \displaystyle \langle \) control-backspace\( \displaystyle \rangle \)
Insert math cell: click blue line between cells
Insert text/HTML cell: shift-click blue line between cells
Delete cell: delete content then backspace
1.2 Command line
com\( \displaystyle \langle \) tab\( \displaystyle \rangle \) complete command
*bar*? list command names containing “bar”
command?\( \displaystyle \langle \) tab\( \displaystyle \rangle \) shows documentation
command??\( \displaystyle \langle \) tab\( \displaystyle \rangle \) shows source code
a.\( \displaystyle \langle \) tab\( \displaystyle \rangle \) shows methods for object a (more: dir(a))
a._\( \displaystyle \langle \) tab\( \displaystyle \rangle \) shows hidden methods for object a
search_doc("string or regexp") fulltext search of docs
search_src("string or regexp") search source code
_ is previous output
1.3 Numbers
Integers: \( \displaystyle \mathbf{Z} =\) ZZ e.g. -2 -1 0 1 10^100
Rationals: \( \displaystyle \mathbf{Q} =\) QQ e.g. 1/2 1/1000 314/100 -2/1
Reals: \( \displaystyle \mathbf{R}\approx \) RR e.g. .5 0.001 3.14 1.23e10000
Polynomials: \( \displaystyle R[x,y]\) e.g. S.<x,y>=QQ[] x+2*y^3
Interval arithmetic: RIF e.g. sage: RIF((1,1.00001))
1.4 Arithmetic
\( \displaystyle ab =\) a*b \( \displaystyle \frac{a} {b} =\) a/b \( \displaystyle a^{b} =\) a^b \( \displaystyle \sqrt{x} =\) sqrt(x)
\( \displaystyle \root{n}\of{x} =\) x^(1/n) \( \displaystyle |x| =\) abs(x) \( \displaystyle \log _{b}(x) =\) log(x,b)
Sums: \( \displaystyle \sum _{i=k}^{n}f(i) =\) sum(f(i) for i in (k..n))
Products: \( \displaystyle \mathop{\mathop{∏ }}\nolimits _{i=k}^{n}f(i) =\) prod(f(i) for i in (k..n))
1.5 Builtin constants and functions
Constants: \( \displaystyle \pi =\) pi \( \displaystyle e =\) e \( \displaystyle i =\) I = i
\( \displaystyle \infty =\) oo = infinity NaN=NaN \( \displaystyle \log (2) =\) log2
\( \displaystyle \varphi =\) golden_ratio
\( \displaystyle \quad γ =\)
euler_gamma
\( \displaystyle 0.915\approx \) catalan
\( \displaystyle 2.685\approx \)
khinchin
\( \displaystyle 0.660\approx \) twinprime
\( \displaystyle 0.261\approx \) merten
\( \displaystyle 1.902\approx \)
brun
Approximate: pi.n(digits=18)\( \displaystyle = 3.14159265358979324\)
Builtin functions: sin cos tan sec csc cot sinh cosh tanh sech csch coth log ln exp ...
2 Symbolic expressions and operations on expressions
2.1 Symbolic expressions
Define new symbolic variables: var("t u v y z")
Symbolic function: e.g. \( \displaystyle f(x) = x^{2}\) f(x)=x^2
Relations: f==g f<=g f>=g f<g f>g
_ is previous output
_+a _-a _*a _/a manipulates equation
Solve \( \displaystyle f(x) = g(x)\) : solve(f(x)==g(x),x)
solve([f(x,y)==0, g(x,y)==0], x,y)
find_root(f(x), a, b) find \( \displaystyle x\in [a,b]\) s.t. \( \displaystyle f(x)\approx 0\)
\( \displaystyle \sum _{i=k}^{n}f(i) =\) sum([f(i) for i in [k..n]])
\( \displaystyle \mathop{\mathop{∏ }}\nolimits _{i=k}^{n}f(i) =\) prod([f(i) for i in [k..n]])
2.2 Defining symbolic expressions
Create symbolic variables:
var("t u theta") or var("t,u,theta")
Use * for multiplication and ^ for exponentiation:
\( \displaystyle 2x^{5} + \sqrt{2} =\) 2*x^5 + sqrt(2)
Typeset: show(2*theta^5 + sqrt(2)) \( \displaystyle \mathrel{→}2θ^{5} + \sqrt{2}\)
2.3 Symbolic functions
Symbolic function (can integrate, differentiate, etc.):
f(a,b,theta) = a + b*theta^2
Also, a “formal” function of theta:
f = function(’f’,theta)
Piecewise symbolic functions:
Piecewise([[(0,pi/2),sin(1/x)],[(pi/2,pi),x^2+1]])

2.4 Python functions
Defining:
def f(a, b, theta=1):
c = a + b*theta^2
return c
Inline functions:
f = lambda a, b, theta = 1: a + b*theta^2
2.5 Simplifying and expanding
Below \( \displaystyle f\) must be symbolic (so not a Python function):
Simplify: f.simplify_exp(), f.simplify_full(),
f.simplify_log(), f.simplify_radical(),
f.simplify_rational(), f.simplify_trig()
Expand: f.expand(), f.expand_rational()
2.6 Equations
Relations: \( \displaystyle f = g\) : f == g, \( \displaystyle f\neq g\) : f != g, \( \displaystyle f\leq g\) : f <= g, \( \displaystyle f\geq g\) : f >= g, \( \displaystyle f < g\) : f < g, \( \displaystyle f > g\) : f > g
Solve \( \displaystyle f = g\) :
solve(f == g, x),
solve([f == 0, g == 0], x,y)
solve([x^2+y^2==1, (x-1)^2+y^2==1],x,y)
Solutions: S = solve(x^2+x+1==0, x, solution_dict=True),
S[0]["x"] S[1]["x"] are the solutions
Exact roots: (x^3+2*x+1).roots(x)
Real roots: (x^3+2*x+1).roots(x,ring=RR)
Complex roots: (x^3+2*x+1).roots(x,ring=CC)
2.7 Factorization
Factored form: (x^3-y^3).factor()
List of (factor, exponent) pairs:
(x^3-y^3).factor_list()
3 Calculus
3.1 Limits
\( \displaystyle \lim _{x\to a}f(x) =\) limit(f(x), x=a)
limit(sin(x)/x, x=0)
\( \displaystyle \lim _{x\to a^{+}}f(x) =\) limit(f(x), x=a, dir=’plus’)
limit(1/x, x=0, dir=’plus’)
\( \displaystyle \lim _{x\to a^{−}}f(x) =\) limit(f(x), x=a, dir=’minus’)
limit(1/x, x=0, dir=’minus’)
3.2 Derivatives
\( \displaystyle \frac{d} {dx}(f(x)) =\) diff(f(x),x) = f.diff(x)
\( \displaystyle \frac{\partial\, } {\partial\, x}(f(x,y)) =\) diff(f(x,y),x)
diff \( \displaystyle =\) differentiate \( \displaystyle =\) derivative
diff(x*y + sin(x^2) + e^(-x), x)
3.3 Integrals
\( \displaystyle \int f(x)dx =\) integral(f,x) = f.integrate(x)
integral(x*cos(x^2), x)
\( \displaystyle \int _{a}^{b}f(x)dx =\) integral(f,x,a,b)
integral(x*cos(x^2), x, 0, sqrt(pi))
\( \displaystyle \int _{a}^{b}f(x)dx\approx \) numerical_integral(f(x),a,b)[0]
numerical_integral(x*cos(x^2),0,1)[0]
assume(...): use if integration asks a question
assume(x>0)
3.4 Taylor and partial fraction expansion
Taylor polynomial, deg \( \displaystyle n\)
about \( \displaystyle a\) :
taylor(f,x,a,n)\( \displaystyle \approx c_{0} + c_{1}(x − a) +\cdots +c_{n}(x − a)^{n}\)
taylor(sqrt(x+1), x, 0, 5)
Partial fraction:
(x^2/(x+1)^3).partial_fraction()
3.5 Numerical roots and optimization
Numerical root: f.find_root(a, b, x)
(x^2 - 2).find_root(1,2,x)
Maximize: find \( \displaystyle (m,x_{0})\)
with \( \displaystyle f(x_{0}) = m\)
maximal
f.find_maximum_on_interval(a, b, x)
Minimize: find \( \displaystyle (m,x_{0})\)
with \( \displaystyle f(x_{0}) = m\)
minimal
f.find_minimum_on_interval(a, b, x)
Minimization: minimize(f, start_point)
minimize(x^2+x*y^3+(1-z)^2-1, [1,1,1])
3.6 Multivariable calculus
Gradient: f.gradient() or f.gradient(vars)
(x^2+y^2).gradient([x,y])
Hessian: f.hessian()
(x^2+y^2).hessian()
Jacobian matrix: jacobian(f, vars)
jacobian(x^2 - 2*x*y, (x,y))
4 Graphics
4.1 2D graphics
line([(\( \displaystyle x_{1}\) ,\( \displaystyle y_{1}\) ),\( \displaystyle \mathop{\mathop{…}}\) ,(\( \displaystyle x_{n}\) ,\( \displaystyle y_{n}\) )],\( \displaystyle options\) )
polygon([(\( \displaystyle x_{1}\) ,\( \displaystyle y_{1}\) ),\( \displaystyle \mathop{\mathop{…}}\) ,(\( \displaystyle x_{n}\) ,\( \displaystyle y_{n}\) )],\( \displaystyle options\) )
circle((\( \displaystyle x\) ,\( \displaystyle y\) ),\( \displaystyle r\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
text("txt",(\( \displaystyle x\) ,\( \displaystyle y\) ),\( \displaystyle options\) )
options as in plot.options, e.g. thickness=\( \displaystyle pixel\) ,
rgbcolor=(\( \displaystyle r\) ,\( \displaystyle g\) ,\( \displaystyle b\) ), hue=\( \displaystyle h\) where \( \displaystyle 0 ≤ r,b,g,h ≤ 1\)
show(graphic, options)
use figsize=[w,h] to adjust size
use aspect_ratio=number to adjust aspect ratio
plot(f(\( \displaystyle x\) ),\( \displaystyle (x,x_{min},x_{max})\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
parametric_plot((f(\( \displaystyle t\) ),g(\( \displaystyle t\) )),\( \displaystyle (t,t_{min},t_{max})\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
polar_plot(f(\( \displaystyle t\) ),\( \displaystyle (t,t_{min},t_{max})\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
combine: circle((1,1),1)+line([(0,0),(2,2)])
animate(list of graphics, options).show(delay=20)
4.2 3D graphics
line3d([(\( \displaystyle x_{1}\) ,\( \displaystyle y_{1}\) ,\( \displaystyle z_{1}\) ),\( \displaystyle \mathop{\mathop{…}}\) ,(\( \displaystyle x_{n}\) ,\( \displaystyle y_{n}\) ,\( \displaystyle z_{n}\) )],\( \displaystyle options\) )
sphere((\( \displaystyle x\) ,\( \displaystyle y\) ,\( \displaystyle z\) ),\( \displaystyle r\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
text3d("txt", (\( \displaystyle x\) ,\( \displaystyle y\) ,\( \displaystyle z\) ), \( \displaystyle options\) )
tetrahedron((\( \displaystyle x\) ,\( \displaystyle y\) ,\( \displaystyle z\) ),\( \displaystyle size\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
cube((\( \displaystyle x\) ,\( \displaystyle y\) ,\( \displaystyle z\) ),\( \displaystyle size\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
octahedron((\( \displaystyle x\) ,\( \displaystyle y\) ,\( \displaystyle z\) ),\( \displaystyle size\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
dodecahedron((\( \displaystyle x\) ,\( \displaystyle y\) ,\( \displaystyle z\) ),\( \displaystyle size\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
icosahedron((\( \displaystyle x\) ,\( \displaystyle y\) ,\( \displaystyle z\) ),\( \displaystyle size\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
plot3d(f(\( \displaystyle x,y\) ),\( \displaystyle (x,x_{b},x_{e})\) , \( \displaystyle (y,y_{b},y_{e})\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
parametric_plot3d((f,g,h),\( \displaystyle (t,t_{b},t_{e})\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
parametric_plot3d((f(\( \displaystyle u,v\) ),g(\( \displaystyle u,v\) ),h(\( \displaystyle u,v\) )),
\( \displaystyle (u,u_{b},u_{e})\) ,\( \displaystyle (v,v_{b},v_{e})\) ,\( \displaystyle options\) )
options: aspect_ratio=\( \displaystyle [1,1,1]\) , color="red"
opacity=0.5, figsize=6, viewer="tachyon"
5 Matrices
5.1 Basic matrix algebra
\( \displaystyle \left (\array{ 1\cr 2} \right ) =\) vector([1,2])
\( \displaystyle \left (\array{ 1& 2\cr 3& 4} \right ) =\) matrix(QQ,[[1,2],[3,4]], sparse=False)
\( \displaystyle \left (\array{ 1& 2& 3\cr 4& 5 & 6} \right ) =\) matrix(QQ,2,3,[1,2,3, 4,5,6])
\( \displaystyle \left |\array{ 1& 2\cr 3& 4} \right | =\) det(matrix(QQ,[[1,2],[3,4]]))
\( \displaystyle Av =\) A*v \( \displaystyle A^{−1} =\) A^-1 \( \displaystyle A^{t} =\) A.transpose()
Solve \( \displaystyle Ax = v\) : A\v or A.solve_right(v)
Solve \( \displaystyle xA = v\) : A.solve_left(v)
Reduced row echelon form: A.echelon_form()
Rank and nullity: A.rank() A.nullity()
Hessenberg form: A.hessenberg_form()
Characteristic polynomial: A.charpoly()
Eigenvalues: A.eigenvalues()
Eigenvectors: A.eigenvectors_right() (also left)
Gram-Schmidt: A.gram_schmidt()
Visualize: A.plot()
LLL reduction: matrix(ZZ,...).LLL()
Hermite form: matrix(ZZ,...).hermite_form()
5.2 Matrix Constructions
Caution: Row, column numbering begins at 0
A = matrix(ZZ, [[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]])
\( \displaystyle 3\times 2\)
over the integers
B = matrix(QQ, 2, [1,2,3,4,5,6])
2 rows from a list, so \( \displaystyle 2\times 3\)
over rationals
C = matrix(CDF, 2, 2, [[5*I, 4*I], [I, 6]])
complex entries, 53-bit precision
Z = matrix(QQ, 2, 2, 0) zero matrix
D = matrix(QQ, 2, 2, 8)
diagonal entries all \( \displaystyle 8\) ,
other entries zero
I = identity_matrix(5)\( \displaystyle 5\times 5\)
identity matrix
J = jordan_block(-2,3)
\( \displaystyle 3\times 3\)
matrix, \( \displaystyle − 2\) on
diagonal, \( \displaystyle 1\) ’s
on super-diagonal var(’x y z’); K = matrix(SR, [[x,y+z],[0,x^2*z]])
symbolic expressions live in the ring SR
L=matrix(ZZ, 20, 80, {(5,9):30, (15,77):-6})
\( \displaystyle 20\times 80\) ,
two non-zero entries, sparse representation
5.3 Matrix Multiplication
u = vector(QQ, [1,2,3]), v = vector(QQ, [1,2])
A = matrix(QQ, [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
B = matrix(QQ, [[1,2],[3,4]])
u*A, A*v, B*A, B^6, B^(-3) all possible
B.iterates(v, 6) produces \( \displaystyle vB^{0},vB^{1},\mathop{\mathop{…}},vB^{5}\)
rows = False moves v to right of matrix powers
f(x)=x^2+5*x+3 then f(B) is possible
B.exp() matrix exponential, i.e. \( \displaystyle \sum _{k=0}^{\infty }\frac{B^{k}}
{k!} \)
5.4 Matrix Spaces
M = MatrixSpace(QQ, 3, 4)
dimension 12 space of \( \displaystyle 3\times 4\)
matrices
A = M([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12])
is a \( \displaystyle 3\times 4\)
matrix, an element of M
M.basis()
M.dimension()
M.zero_matrix()
5.5 Matrix Operations
5*A+2*B linear combination
A.inverse(), also A^(-1), ~A
ZeroDivisionError if singular
A.transpose()
A.antitranspose() transpose + reverse orderings
A.adjoint() matrix of cofactors
A.conjugate() entry-by-entry complex conjugates
A.restrict(V) restriction on invariant subspace V
5.6 Row Operations
Row Operations: (change matrix in place)
Caution: first row is numbered 0
A.rescale_row(i,a) a*(row i)
A.add_multiple_of_row(i,j,a) a*(row j) + row i
A.swap_rows(i,j)
Each has a column variant, row\( \displaystyle →\) col
For a new matrix, use e.g. B = A.with_rescaled_row(i,a)
5.7 Echelon Form
A.echelon_form(), A.echelonize(), A.hermite_form()
Caution: Base ring affects results
A = matrix(ZZ,[[4,2,1],[6,3,2]])
B = matrix(QQ,[[4,2,1],[6,3,2]])
| A.echelon_form() | B.echelon_form() |
| \( \displaystyle \left (\array{ 2& 1& 0\cr 0 & 0 & 1} \right )\) | \( \displaystyle \left (\array{ 1& \frac{1} {2}& 0\cr 0 & 0 & 1 } \right )\) |
A.pivots() indices of columns spanning column space
A.pivot_rows() indices of rows spanning row space
5.8 Pieces of Matrices
Caution: row, column numbering begins at 0
A.nrows()
A.ncols()
A[i,j] entry in row i and column j
Caution: OK: A[2,3] = 8, Error: A[2][3] = 8
A[i] row i as immutable Python tuple
A.row(i) returns row i as Sage vector
A.column(j) returns column j as Sage vector
A.list() returns single Python list, row-major order
A.matrix_from_columns([8,2,8])
new matrix from columns in list, repeats OK
A.matrix_from_rows([2,5,1])
new matrix from rows in list, out-of-order OK
A.matrix_from_rows_and_columns([2,4,2],[3,1])
common to the rows and the columns
A.rows() all rows as a list of tuples
A.columns() all columns as a list of tuples
A.submatrix(i,j,nr,nc)
start at entry (i,j), use nr rows, nc cols
A[2:4,1:7], A[0:8:2,3::-1] Python-style list slicing
5.9 Combining Matrices
A.augment(B) A in first columns, B to the right
A.stack(B) A in top rows, B below
A.block_sum(B) Diagonal, A upper left, B lower right
A.tensor_product(B) Multiples of B, arranged as in A
5.10 Scalar Functions on Matrices
A.rank()
A.nullity() == A.left_nullity()
A.right_nullity()
A.determinant() == A.det()
A.permanent()
A.trace()
A.norm() == A.norm(2) Euclidean norm
A.norm(1) largest column sum
A.norm(Infinity) largest row sum
A.norm(’frob’) Frobenius norm
5.11 MatrixProperties
.is_zero() (totally?), .is_one() (identity matrix?),
.is_scalar() (multiple of identity?), .is_square(),
.is_symmetric(), .is_invertible(), .is_nilpotent()
5.12 Eigenvalues
A.charpoly(’t’) no variable specified defaults to x
A.characteristic_polynomial() == A.charpoly()
A.fcp(’t’) factored characteristic polynomial
A.minpoly() the minimum polynomial
A.minimal_polynomial() == A.minpoly()
A.eigenvalues() unsorted list, with mutiplicities
A.eigenvectors_left() vectors on left, _right too
Returns a list of triples, one per eigenvalue:
e: the eigenvalue
V: list of vectors, basis for eigenspace
n: algebraic multiplicity
A.eigenmatrix_right() vectors on right, _left too
Returns two matrices:
D: diagonal matrix with eigenvalues
P: eigenvectors as columns (rows for left version)
has zero columns if matrix not diagonalizable
5.13 Solutions to Systems
A.solve_right(B) _left too
is solution to A*X = B, where X is a vector or matrix
A = matrix(QQ, [[1,2],[3,4]])
b = vector(QQ, [3,4])
then A\b returns the solution (-2, 5/2)
6 Linear algebra
Vector space \( \displaystyle K^{n} =\) K^n e.g. QQ^3 RR^2 CC^4
Subspace: span(vectors, field )
E.g., span([[1,2,3], [2,3,5]], QQ)
Kernel: A.right_kernel() (also left)
Sum and intersection: V + W and V.intersection(W)
Basis: V.basis()
Basis matrix: V.basis_matrix()
Restrict matrix to subspace: A.restrict(V)
Vector in terms of basis: V.coordinates(vector)
6.1 Vector Constructions
Caution: First entry of a vector is numbered 0
u = vector(QQ, [1, 3/2, -1]) length 3 over rationals
v = vector(QQ, {2:4, 95:4, 210:0})
211 entries, nonzero in entry 4 and entry 95, sparse
6.2 Vector Operations
u = vector(QQ, [1, 3/2, -1])
v = vector(ZZ, [1, 8, -2])
2*u - 3*v linear combination
u.dot_product(v)
u.cross_product(v) order: u\( \displaystyle \times \) v
u.inner_product(v) inner product matrix from parent
u.pairwise_product(v) vector as a result
u.norm() == u.norm(2) Euclidean norm
u.norm(1) sum of entries
u.norm(Infinity) maximum entry
A.gram_schmidt() converts the rows of matrix A
6.3 Vector Spaces
U = VectorSpace(QQ, 4) dimension 4, rationals as field
V = VectorSpace(RR, 4) “field” is 53-bit precision reals
W = VectorSpace(RealField(200), 4)
“field” has 200 bit precision
X = CC^4 4-dimensional, 53-bit precision complexes
Y = VectorSpace(GF(7), 4) finite
Y.finite() returns True
len(Y.list()) returns \( \displaystyle 7^{4} = 2401\)
elements
6.4 Vector Space Properties
V.dimension()
V.basis()
V.echelonized_basis()
V.has_user_basis() with non-canonical basis?
V.is_subspace(W) True if W is a subspace of V
V.is_full() rank equals degree (as module)?
Y = GF(7)^4, T = Y.subspaces(2)
T is a generator object for 2-D subspaces of Y
[U for U in T] is list of 2850 2-D subspaces of Y
6.5 Constructing Subspaces
span([v1,v2,v3], QQ) span of list of vectors over ring
For a matrix A, objects returned are
vector spaces when base ring is a field
modules when base ring is just a ring
A.left_kernel() == A.kernel() right_ too
A.row_space() == A.row_module()
A.column_space() == A.column_module()
A.eigenspaces_right() vectors on right, _left too
Pairs, having eigenvalue with its right eigenspace
If V and W are subspaces
V.quotient(W) quotient of V by subspace W
V.intersection(W) intersection of V and W
V.direct_sum(W) direct sum of V and W
V.subspace([v1,v2,v3]) specify basis vectors in a list
6.6 Dense versus Sparse
Note: Algorithms may depend on representation
Vectors and matrices have two representations
Dense: lists, and lists of lists
Sparse: Python dictionaries
.is_dense(), .is_sparse() to check
A.sparse_matrix() returns sparse version of A
A.dense_rows() returns dense row vectors of A
Some commands have boolean sparse keyword
6.7 Rings
Note: Many algorithms depend on the base ring
<object>.base_ring(R) for vectors, matrices,…
to determine the ring in use
<object>.change_ring(R) for vectors, matrices,…
to change to the ring (or field), R,
R.is_ring(), R.is_field()
R.is_integral_domain(), R.is_exact()
Some ring and fields
ZZ integers, ring
QQ rationals, field
QQbar algebraic field, exact
RDF real double field, inexact
RR 53-bit reals, inexact
RealField(400) 400-bit reals, inexact
CDF, CC, ComplexField(400) complexes, too
RIF real interval field
GF(2) mod 2, field, specialized implementations
GF(p) == FiniteField(p) p prime, field
Integers(6) integers mod 6, ring only
CyclotomicField(7) rationals with
7\( \displaystyle ^{th}\) root
of unity
QuadraticField(-5, ’x’) rationals adjoin
x=\( \displaystyle \sqrt{−5}\)
SR ring of symbolic expressions
6.8 Vector Spaces versus Modules
A module is “like” a vector space over a ring, not a field
Many commands above apply to modules
Some “vectors” are really module elements
7 Specials
7.1 Python modules
import module_name
module_name.\( \displaystyle \langle \) tab\( \displaystyle \rangle \) and help(module_name)
7.2 Profiling and debugging
time command: show timing information
timeit("command"): accurately time command
t = cputime(); cputime(t): elapsed CPU time
t = walltime(); walltime(t): elapsed wall time
%pdb: turn on interactive debugger (command line only)
%prun command: profile command (command line only)